Sources:
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lHfAGaU-HkE (Ivan Obodyanskyy)
- CakePHP 2.0 Docs: https://book.cakephp.org/2.0/en/
Directory Structure
Structure of the main Cake folder
/cake/
./app (User application and files here ...)
./lib (CakePHP Core files are stored here)
./plugins ()
./vendors (Third party PHP Libraries)Structure of /cake/app folder. This is is where most of user development takes place. Cake emphasizes on convention over configuration.
/cake/app/
./Config - Config files used by Cake php
- database connection details, bootstrapping, etc
./Console - Console tasks for your application
./Controller - Application controllers and components
./Lib - Internally developed libraries only
./Locale - Internationalisation files
./Model - Application models
./Plugin - Plugin packages
./Tests - Application test cases
./tmp - Cake temporary files (sessions, logs, etc)
./Vendor - Third party classes / libraries. Use App Import function.
./View - Presentation files. Elements, error pages, helpers and layouts
./webroot - Point DocumentRoot for the application here.
- Also place CSS, Javascript and images here.Installation
- Check system requirements for your version of Cake being installed
- Change the value of
Security.saltin/app/Config/core.php - change the value of
Security.cipherSeedin/app/Config/core.phpto a numeric (digits only) seed value - PHP minimum version must be satisfied
/app/tmpdirectory must be writable (chmod 777)- Set database connection settings,
/app/Config/database.php
Run CakePHP Server From Command Line
Navigate to your project root folder and run the cake serve command as below
cd /cakephp-folder/
## Start Cake Http Server at port 8080
$ ./lib/Cake/Console/cake serve -p 8080
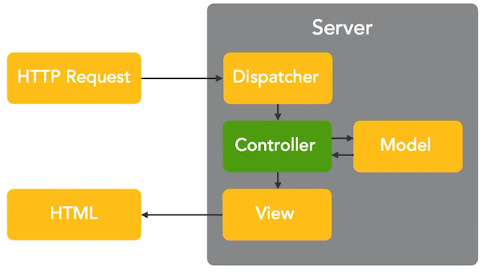
CakePHP HTTP Request Handling
Dispatcher -> Controller -> Model -> View -> html
When a user makes a request, the request goes to the dispatcher which makes decisions about which controller to call. The controllers then calls a model (if required), then the controller sends the results of the request to the view
CakePHP Conventions
CakePHP favours conventions over configurations.
- CakePHP serve as guidelines only. Developers are free to do things differently
- Following conventions is recommended for faster development speed
- Conventions makes onboarding new team members easier.
By following a convention, developers avoid maintaining a log of configuration files.
CakePHP Controllers
- Class names must be plural, camel cased, and must end with controller e.g PeopleController, LatestArticlesController.
- When a web request specifies a controller and does not specify an action, the
index()method is called. - A reguest to
www.example.com/apples/callsApplesControllerindex() method - A requet to
www.example.com/apples/viewcallsApplesControllerview() method ApplesControllerwill be defined in the fileApplesController.php- Controller names become part of the URL naming convention. Choose controller names carefully.
- Url
red_apples/go_pick/is mapped toRedApplesController's go_pick() action - If you have a file or a directory in the webroot folder that shares a name with a controller or method, Cake will go to the file or directory and not the Controller.
- Methods/Actions in a controller that have been prefixed with an underscore are not accessible via the web.
class NewsController {
protected function _findNewArticles () {}
public function latest() {
$this->_findNewArticles();
}
}
// www.example.com/news/latest # will be successful
// www.example.com/news/_findNewArticles # will fail as action name starts with an underscore.CakePHP Model and Database Conventions
- Model class names are singular and CamelCased (Person, BigPerson, ReallyBigPerson)
- Database table names corresponding to models are plural and snake cased, (people, big_people, really_big_people)
- Database table field names use snake casing too (first_name)
- Foreing keys in hasMany, belongsTo, or hasOne relationships are recognised by default as the (singular) name of the related table followed by _id.
- If a Baker hasMany Cakes, cakes table will refer to the bakers table via baker_id foreign key.
- For table
category_typesthe foreign key will becategory_type_id - For many-many database tables, the table name must include model names for both tables in alphabetical order. E.g. a join table for
recipestable andingredientstable will be namedingredients_recipes. Database table fields (ingredients_recipes.id, ingredients_recipes.ingredient_id, ingredients_recipes.recipe_id), HABTM
View Conventions
- View template files are names after the controller actions they display.
- The view file structure for
PeopleController->getReady()will be/app/View/People/get_ready.cpt
Looking at all conventions at once
Database table: people
Model class: Person, "/app/Model/Person.php"
Controller class: PeopleController, "/app/Controller/PeopleController.php"
View Template: /app/Views/People/index.cptCakePHP Layouts
- Think of layout as Themes. Layout files are placed in the folder
/app/View/Layoutswith file extension.cpt - The default layout file out of the box is
default.cpt. Pages use the default layout used by/app/View/Pages/home.cptpage. Edit contents of the home.cpt file to see the effects. - If you want to change the default layout, you can edit default.cpt or create new file in its place and then and some code to AppController.
// app/Controller/AppController.php
// ...
class AppController extends Controller {
// beforeFilter is executed first in Cake classes before
// other functions in the class are called.
public function beforeFilter()
{
# Change default layout to Main.ctp
$this->layout = 'main';
}
}CakePHP Controllers
Controllers contain the business logic. Methods to retrieve data, filter data, and other user related actions must be placed in Controllers.
Create a controller called UsersController populated with users in an array
<?php
// app/Controller/UsersController.php
class UsersController extends AppController
{
public function index () {
$this->set('page_title', 'Fun with Users');
$users = [
['id' => '01', 'first_name' => 'Sue', 'last_name' => 'Ja'],
['id' => '02', 'first_name' => 'Pat', 'last_name' => 'Lo'],
['id' => '03', 'first_name' => 'Cra', 'last_name' => 'Ha'],
['id' => '04', 'first_name' => 'Gie', 'last_name' => 'Cu']
];
// make users available to view
$this->set('users', $users);
}
}CakePHP Components
Each time you are duplicating code in a single Controller or across controllers, you should consider extracting the duplicate code out to a Component.
Sample component
<?php
# File: /app/Controller/Component/MathComponent.php
App::uses('Component', 'Controller');
class MathComponent extends Component
{
// Given an array of data, extract a column, and sum numbers in the column
// Assume data contains sales figures
public function sum($data, $column) {
$total = Hash::extract($data, "{n}.Sale.$column");
return array_sum($total);
}
}Using MathComponent in a controller
<?php
App::uses('AppController', 'Controller');
class UsersController extends AppController
{
// Use the Math custom component
public $components = [
'Math',
];
public function index() {
// Use Maths component
$sales = $this->Sale->find('all');
$total = $this->Math->sum($sales, 'price');
$this->set('sales', $sales);
}
}
CakePHP Views
Views must be used to present data to the user. Views must not process data. That is the job of a controller.
Create a view for UsersController above to display list of users in a table.
<?php # /app/View/Users/index.ctp ?>
<h1 style="font-size: 2em;"> <?php echo $page_title ?> </h1>
<table>
<tr>
<th>ID</th> <th>First name</th> <th>Last name</th>
</tr>
<?php
foreach($users as $user) {
$htm = "<td>{$user['id']}</td>";
$htm .= "<td>{$user['first_name']}</td>";
$htm .= "<td>{$user['last_name']}</td>";
echo "<tr> $htm </tr>";
}
?>
</table>Navigate to http://cake.local/users to view users.
CakePHP Model
Models contain database related methods like Create, Read, Delete, Update, and Validation.
- Create a database table of Users.
CREATE TABLE `cakedb`.`users` (
`id` INT NOT NULL,
`username` VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL,
`password` VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL,
`name` VARCHAR(45) NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`, `username`, `password`));Insert some data into the new database table
INSERT INTO cakedb.users
VALUES
(1, 'maria', 'pass', 'Mary Katana'),
(2, 'lucas', '1234', 'Luke Jambo'),
(3, 'maloi', 'pass', 'Lidan Bamai');Create a CakePHP User Model
<?php
// app/Model/User.php
class User extends AppModel
{
//
}Some controllers do not have a view. They may simply send back a JSON response to the calling API.
class UsersController extends AppController
{
public $autoRender = false;
public function index() {
$users = [
['id' => '01', 'first_name' => 'Sue', 'last_name' => 'Ja'],
['id' => '02', 'first_name' => 'Pat', 'last_name' => 'Lo'],
['id' => '03', 'first_name' => 'Cra', 'last_name' => 'Ha'],
['id' => '04', 'first_name' => 'Gie', 'last_name' => 'Cu']
];
// Response as JSON, no view
$this->response->type('json');
$this->response->body(json_encode($users));
// $this->response->body(var_dump($books)); // dump raw data to response
}
}Modify the UsersController to retrieve data from the database
<?php
// app/Controller/UsersController.php
class UsersController extends AppController
{
public function index () {
$this->set('page_title', 'Users from database');
// Get users from database
$users = $this->User->find('all');
// // make users available to view
$this->set('users', $users);
}
}Modify the index view, the return data structure has changed. Debug statements allow us to inspect the users variable coming from the controller.
<?php # /app/View/Users/index.ctp ?>
<?php
# debug users
// debug($users);
?>
<h1 style="font-size: 2em;"> <?php echo $page_title ?> </h1>
<table>
<tr>
<th>ID</th> <th>User name/th> <th>Full name</th>
</tr>
<?php
foreach($users as $key => $value) {
// debug($value);
// break;
$user = $value['User'];
$htm = "<td>{$user['id']}</td>";
$htm .= "<td>{$user['username']}</td>";
$htm .= "<td>{$user['name']}</td>";
echo "<tr> $htm </tr>";
}
// alt syntax, does the same thing only cleaner
foreach ($users as $user) {
$htm = "<td> {$user['User']['id']} </td>";
$htm .= "<td> {$user['User']['username']} </td>";
$htm .= "<td> {$user['User']['name']} </td>";
echo "<tr> $htm </tr>";
}
?>
</table>To retrieve details of one User if a user navigates to '/Users/view/1' where 1 is an id in the database
- add a view() action to Users controller.
<?php
// app/Controller/UsersController.php
class UsersController extends AppController
{
// ...
public function view ($id) {
$this->set('page_title', 'Selected user');
$users = $this->User->find(
"first",
array('conditions' => ['id' => $id])
);
# alternative use findById() magic method
# $users = $this->User->findById($id);
# using read methods
# $users = $this->User->read(null, $id); # null returns all fields
$this->set('user', $users);
}
}Create view.ctp file
<?php # app/View/Users/view.ctp ?>
<h1 style="font-size: 2em;"> <?php echo $page_title ?> </h1>
<table>
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>User name </th>
<th>Full name</th>
<th>Password</th>
</tr>
<?php
$htm = "<td> {$user['User']['id']} </td>";
$htm .= "<td> {$user['User']['username']} </td>";
$htm .= "<td> {$user['User']['name']} </td>";
$htm .= "<td> {$user['User']['password']} </td>";
echo "<tr> $htm </tr>";
?>
</table>Save/Insert New user to Database
Modify UsersController.php and create an add() method.
<?php
// app/Controller/UsersController.php
class UsersController extends AppController
{
// ....
// save user data to database
public function add () {
$this->set('page_title', 'Create user');
if ($this->request->isPost()) {
if ($this->User->save($this->request->data)) {
// successfully saved
$this->Session->setFlash(__("New user created successfully."));
$this->redirect(['action' => 'index']);
} else {
// failed
$this->Session->setFlash(__("Failed to create user"));
}
}
}
}Create an add.ctp view
<?php
// app/View/Users/add.ctp
// use Form helpers to create a form
echo $this->Form->create('User');
echo $this->Form->input('id');
echo $this->Form->input('username');
echo $this->Form->input('password');
echo $this->Form->input('name');
echo $this->Form->end('Submit');Modify Field Values Before Save
Use Model::set() to change values of a model before save
<?php
// Change one field at a time
// Change user's title to doctor and save
$this->User->set('title', 'Doctor');
$this->User->save();
// Set multiple fields at a time and save
$this->User->set([
'firstname' => 'Lucas',
'title' => 'Doctor',
'dob' => '1980-01-01'
]);
$this->User->save();
// get ID of newly saved record
$userId = $this->User->id;Data Validation
Validation rules are added to the Model within the constructor.
Example below showing how to validates our User model
<?php
// app/Model/User.php
class User extends AppModel
{
public function __construct($id = null, $table = null, $ds = null)
{
parent::__construct($id, $table, $ds);
$this->validate = array (
'username' => [
'rule' => 'alphaNumeric',
'allowEmpty' => false,
'message' => __('must be alpha numeric')
],
'password' => [
'rule' => ['minLength' => '5'],
'allowEmpty' => false,
'message' => __('Try a longer password')
],
'name' => [
'rule' => 'alphaNumeric',
'allowEmpty' => false,
'message' => __('must be alpha numeric')
]
);
}
}CakePHP Behaviours
Behaviours in CakePHP refers to helpers (or logic) than can be used across multiple models. If you are duplicating code in a model or across Models, extract the duplicate code to a Behaviour class.
Misc notes
// Create a link to a model action.
// this code must go in a view template
<tr><td>
<?php // view link
// e.g. http://cake.local/topics/view/1
echo $this->HTML->link(
$data['Topic']['title], array(
'controller' => 'topics',
'action' => 'view',
$data['Topic']['id']
)
);
?>
</td></tr>
<tr><td>
<?php // Delete link
// e.g. http://cake.local/topics/delete/1
echo $this->Form->postLink(
'Delete',
array(
'controller' => 'topics',
'action' => 'delete',
$data['Topic']['id']
),
array(
'confirm' => 'Are you sure?'
)
);
?>
</td></tr>
/// Delete method in TopicsController
public function delete($id)
{
$this->Topic->id = $id;
if ($this->request->is(['post', 'put']) {
$this->Topic->delete();
// $this->Session->setFlash('Topi deleted successfully');
// $this->redirect('index');
return true;
}
return false;
}Model: Sample User model, methods and properties
Delete a user given an ID
<?php
App::uses('AppModel', 'Model');
App::uses('SimplePasswordHasher', 'Controller/Component/Auth');
class User extends AppModel {
public $validate = array(
'username' => array(
'required' => array(
'rule' => 'notEmpty',
'message' => 'Please enter a username'
)
),
);
//
public function beforeSave($options = []) {
if (!parent::beforeSave($options)) {
return false;
}
$pwd = $this->data[$this->alias]['password'];
if (isset($pwd)) {
$this->data[$this->alias]['password'] = (new SimplePasswordHasher())->hash($pwd);
}
return true;
}
// Delete user
// Source: CakePHP 2 Essential Training
public function delete($id = null) {
$this->User->id = $id;
if (!$this->User->exists()) {
throw new NotFoundException(__('Invalid user'));
}
// important! Prevents users scrapping your site to delete data
// if they accidentally hit this endpoint
$this->request->allowMethod('post', 'delete');
if ($this->User->delete()) {
$this->Flash->success(__('User has been deleted'));
} else {
$this->Flash->error(__('Could not delete user'));
}
return $this->redirect(
['action' => 'index'];
)
}
// create a virtual field called full_name
// concatenate firstname and lastname using SQL commands
public $virtualFields = [
'full_name' => '`firstname` + ` ` + `lastname`',
];
}
Paginator
Source: CakePHP 2 Essential Training Add this method to a controller.
<?php
App::uses('AppController', 'Controller');
class UsersController extends AppController
{
// Components that must be available to very controller your app must be defined in AppController.php
// Use the Paginator component
public $components = [
'Paginator',
];
public function index() {
// Paginate
$this->Paginator->settings = [
'limit' => 25,
'order' => array('created' => 'DESC');
];
$this->set('users', $this->Paginator->paginate());
}
}